Learning Outcomes
i. Compare the composition of inspired and expired air.
ii. Understand how gas exchange in the lungs is essential for maintaining pH balance and metabolic homeostasis.
iii. Recognize the role of the respiratory system in regulating blood gases.
i. Composition of Inspired and Expired Air
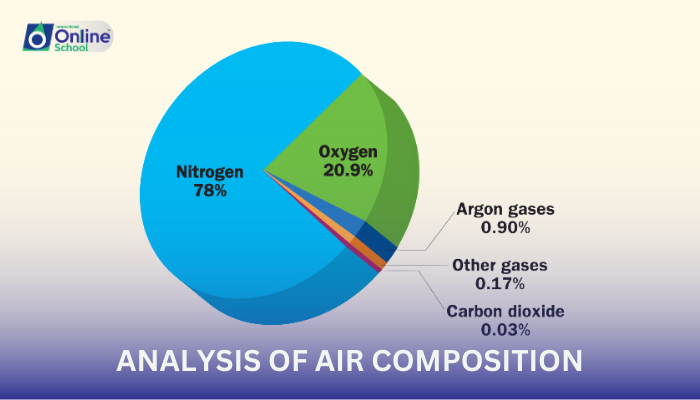
Inspired Air: The air we breathe in is rich in oxygen, with an average concentration of about 21%, and contains only around 0.04% carbon dioxide. It also consists of nitrogen (approximately 78%) and trace amounts of other gases.
Expired Air: The air we breathe out contains a lower concentration of oxygen, about 16%, and a higher concentration of carbon dioxide, around 4%. The composition of expired air reflects the gaseous exchange that has occurred in the lungs.
ii. Gas Exchange and pH Balance
Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Exchange: In the alveoli of the lungs, oxygen from inspired air is transferred to the blood, and carbon dioxide from the blood is transferred to the lungs to be exhaled. This exchange is driven by the differences in partial pressures of these gases in the alveoli and blood.
Maintaining pH Balance: Carbon dioxide is acidic when dissolved in blood and can lower the blood's pH. The body regulates the removal of carbon dioxide to maintain a balanced blood pH of around 7.4. The respiratory system plays a critical role in this regulation by adjusting the rate and depth of breathing in response to blood pH levels.
iii. Metabolic Homeostasis
Role of Respiratory System: The respiratory system helps maintain metabolic homeostasis by regulating the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. Oxygen is vital for cellular respiration, which produces the energy cells need to function, while the removal of carbon dioxide prevents acidosis, which can interfere with cell operations.
Feedback Mechanisms: Chemoreceptors in the body detect changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels and pH, and send signals to the brain to adjust the breathing rate and depth accordingly.
In conclusion, the comparison of inspired and expired air illustrates the body's efficient mechanism for exchanging gases to sustain life. This exchange is not only crucial for providing oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide but also for maintaining the body's pH balance and metabolic homeostasis. Understanding these processes highlights the importance of the respiratory system in regulating the internal environment and ensuring the body's overall function and health.